Overcoming Challenges in Migrating to High Density 400G Data Centers
The evolution of data centers to support advanced storage and computing requirements introduces a set of new challenges in terms of bandwidth, transmission distance, power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. As businesses experience rapid growth, the demand for upgraded connectivity within data centers becomes more pressing. Let’s delve into the common challenges encountered during the migration to high density 400G data centers and explore innovative solutions.
Network Bandwidth Problem
The relentless expansion of data center operations necessitates an immediate upgrade in bandwidth capacity and the construction of new data center networks. As data flows continue to surge, the demand for higher network bandwidth becomes paramount to accommodate the increasing data traffic.
High Power Consumption
One of the critical challenges is the elevated power consumption associated with high-density data centers. This issue not only affects heat dissipation and overall reliability but also contributes to mounting heat dissipation pressure. Managing power consumption efficiently is vital for maintaining a stable and sustainable data center environment.
Limited Budget
Migrating to high-density data centers can significantly raise maintenance costs in the later stages, thereby increasing overall operating expenses. Balancing the need for advanced infrastructure upgrades with budget limitations is a key concern for data center operators.
Upgrading to 400G Data Centers
To address these challenges, the transition from 100G to 400G data centers emerges as a pivotal solution. Several strategies can be employed for a smooth migration:
1. Upgrade from 100G to 400G: Transitioning to 400G data centers involves enhancing network capabilities to handle higher data volumes while maintaining seamless connectivity. This upgrade ensures data centers can keep pace with growing demands.
2. 400G Data Center Using DR4: Deploying Data Center Interconnect (DCI) solutions based on DR4 architecture optimizes transmission capacity and reduces power consumption, contributing to enhanced overall efficiency.
3. 400G Data Center Using SR8: Implementing SR8 technology allows for the efficient handling of network traffic, accommodating the surging demands for seamless and high-speed data transfer.
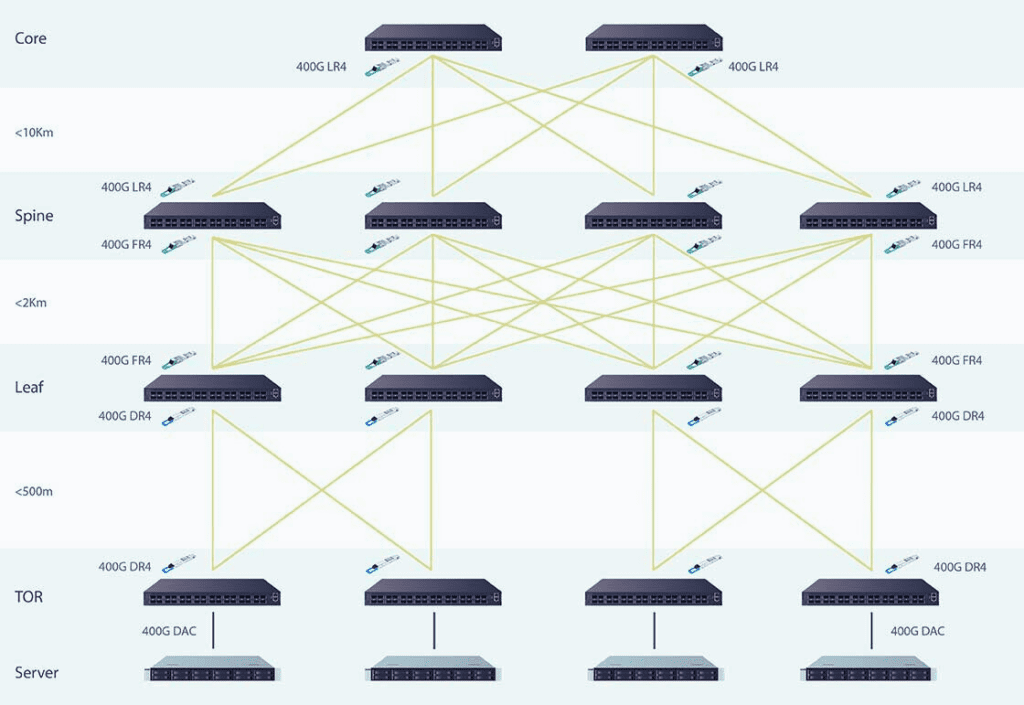
Key Benefits
Embracing the shift to high density 400G data centers offers several key benefits:
High Density: Deploying QSFPDD modules in high density effectively boosts transmission capacity, ensuring data centers can manage substantial data flows seamlessly. Moreover, this facilitates a smooth upgrade path from 100G to 400G, future-proofing data center operations.
Low Power Consumption: Leveraging smaller DSP chips enhances product reliability while minimizing power consumption. Additionally, Dynamic Demultiplexer (DDM) technology simplifies network operation and maintenance, contributing to optimized energy usage.
Flexible Deployment: The ability to connect new 400G sites to legacy 100G sites through 4x100G breakout provides flexibility in network expansion. This approach allows data centers to upgrade based on existing infrastructure, thus yielding significant cost savings.
In conclusion, migrating to high density 400G data centers presents both challenges and opportunities for data center operators. By addressing bandwidth constraints, power consumption issues, and budget limitations, while leveraging the benefits of seamless upgrades, the data center industry can embrace the transformative potential of advanced connectivity solutions.



